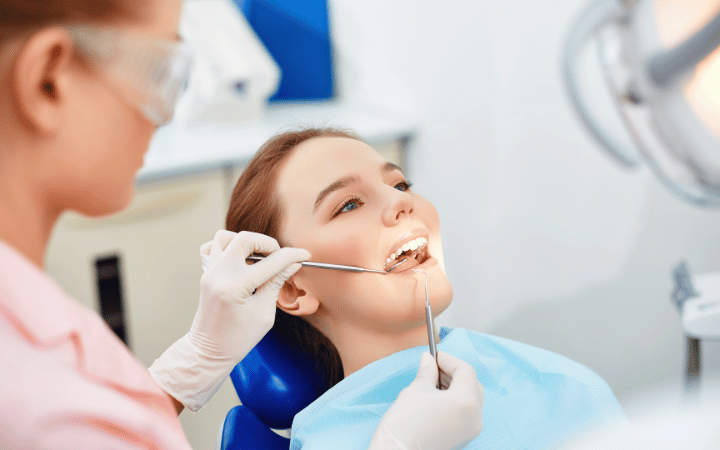
Gingivitis, a common and mild form of gum disease, affects a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives. Characterized by inflammation of the gums, it serves as a crucial warning sign that your oral health needs immediate attention.
Though often overlooked in its early stages due to its subtle symptoms, understanding gingivitis is essential for preventing its progression into more severe periodontal diseases, which can lead to tooth loss and other serious health complications.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, an inflammatory condition affecting the tissues that surround and support your teeth. Primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth—gingivitis is marked by swollen, red gums that may bleed easily when you brush or floss. Unlike more advanced stages of gum disease, gingivitis does not typically affect the bone structure that supports your teeth and, therefore, is reversible with proper dental care.
At its core, gingivitis occurs when the immune system responds to the plaque buildup on teeth. This immune response leads to inflammation, which, if left untreated, can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can damage the soft tissue and bone that support your teeth. However, because gingivitis does not usually cause pain, many individuals may not realize they have it, underscoring the importance of regular dental check-ups.
Understanding the cause of gingivitis is crucial for prevention. Plaque forms on your teeth daily and consists of bacteria, mucus, and other particles. Brushing and flossing regularly help remove plaque, but plaque that is not removed can harden into tartar, a calcified material that dental professionals need to remove. Tartar can further irritate the gum line, leading to gingivitis.
Recognizing gingivitis early on is vital for preventing its progression. By maintaining a rigorous oral hygiene routine and visiting your dentist regularly, you can help protect yourself against the potential complications associated with untreated gingivitis and preserve your overall oral health.
Causes of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene that allows plaque to build up on the teeth and harden, leading to inflammation of the surrounding gum tissues. However, several factors can increase the risk of developing gingivitis, including:
Plaque Buildup: The main culprit behind gingivitis is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria and food particles that forms constantly on your teeth. If not removed through daily brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, further exacerbating gum inflammation and making it more challenging to remove future plaque.
Smoking or Chewing Tobacco: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for gingivitis, as it can reduce the body’s ability to fight infection, including those that start in the gums.
Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can impair the body’s immune system, making it harder to fight off the bacteria that cause gingival inflammation.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those occurring during pregnancy, puberty, menopause, and monthly menstruation, can make gums more sensitive and more susceptible to gingivitis.
Medical Conditions: Certain diseases and conditions, including diabetes, cancer, and HIV, can affect the health of your gums. Diabetes, in particular, can make individuals more prone to infections, including gum disease.
Medications: Some medications can affect oral health because they lessen saliva flow, which has a protective effect on teeth and gums. Medications that cause abnormal growth of gum tissue may also contribute to gingivitis.
Genetic Susceptibility: Some people are more prone to gum disease than others, due to their genetic makeup. If you have a family history of dental disease, you may be at a higher risk for developing gingivitis.
Age: The risk of gingivitis increases with age, due to the cumulative effects of plaque buildup and potential neglect of oral hygiene over the years.
Poor Dental Care: Inadequate brushing and flossing, failing to remove plaque and tartar, and not visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings are direct pathways to gingivitis.
Understanding these causes is the first step towards preventing gingivitis. By addressing these risk factors, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing gum disease and ensure the health of your gums and teeth. Regular dental visits and maintaining a diligent oral hygiene routine are paramount in keeping gingivitis at bay.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Gingivitis often begins without pain, making it difficult for individuals to recognize they have a problem until it escalates. Being aware of the early signs and symptoms of gingivitis can help you seek treatment promptly, preventing the condition from advancing to a more severe stage of gum disease. Common symptoms include:
Bleeding Gums: One of the hallmark signs of gingivitis is bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. Your gums might also bleed when you eat something hard or crunchy. Healthy gums should not bleed from regular cleaning or eating.
Red, Swollen Gums: Gums affected by gingivitis often appear red and swollen, deviating from their healthy pink color and firm texture. This inflammation can make your gums tender to the touch.
Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth can also indicate gingivitis. The bacteria that cause the inflammation can produce odors, leading to halitosis (chronic bad breath).
Receding Gums: Gingivitis can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, making your teeth appear longer than normal. This gum recession can lead to sensitivity and other dental issues.
Soft Gums: Healthy gums are firm and resist movement. Gingivitis can cause your gums to become soft and easily movable.
Sensitive Teeth: As the gums recede and the root of the tooth becomes exposed, you may experience increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and beverages.
It’s important to note that gingivitis can progress without any symptoms at all. For some people, the disease advances silently until it becomes periodontitis, a more serious infection that can lead to tooth loss. This is why regular dental check-ups are crucial, as a dentist can detect signs of gingivitis early, even when symptoms are not yet apparent.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, it’s essential to schedule a visit with your dentist. Early detection and treatment can reverse the effects of gingivitis and restore your oral health. Remember, gingivitis is preventable and treatable with proper oral hygiene and regular dental care.
Preventing Gingivitis
Preventing gingivitis is largely within your control and revolves around maintaining good oral hygiene and making healthy lifestyle choices. By taking proactive steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing gingivitis and ensure the long-term health of your gums and teeth. Here are key strategies for gingivitis prevention:
Maintain Excellent Oral :Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque. This is the cornerstone of preventing gingivitis, as it directly combats the primary cause: plaque buildup.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are crucial for removing tartar that can’t be eliminated by brushing and flossing alone. Your dentist can also spot early signs of gingivitis and other oral health issues before they become serious.
Use Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Incorporating an antimicrobial mouthwash into your daily oral hygiene routine can help reduce the bacteria in your mouth, offering an additional layer of protection against gingivitis.
Eat a Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supports your immune system and promotes oral health. Foods high in vitamin C and calcium, in particular, can help keep your gums healthy.
It’s important to note that gingivitis can progress without any symptoms at all. For some people, the disease advances silently until it becomes periodontitis, a more serious infection that can lead to tooth loss. This is why regular dental check-ups are crucial, as a dentist can detect signs of gingivitis early, even when symptoms are not yet apparent.
Preventing gingivitis is about establishing and maintaining good oral care habits. By taking these steps, you not only protect your gums but also contribute to your overall health and well-being. Remember, healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy smile.
Conclusion
Gingivitis, while a common oral health issue, is both preventable and reversible with proper care. Understanding the causes and symptoms of gingivitis is the first step toward safeguarding your oral health. By visiting your dentist regularly, using antimicrobial mouthwash and eating a balanced diet, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing this condition.
Remember, the health of your gums is integral to your overall well-being. Taking proactive steps to prevent gingivitis not only ensures the longevity of your teeth but also contributes to your general health. If you notice any signs of gingivitis, it’s important to consult with a dental professional promptly. Early detection and treatment can prevent the progression of gum disease and keep your smile bright and healthy.
Maintaining oral health is a lifelong commitment. By adopting good oral hygiene practices and making informed lifestyle choices, you can enjoy the benefits of a healthy mouth for years to come. Let’s prioritize our oral health and take the necessary steps to prevent gingivitis together.