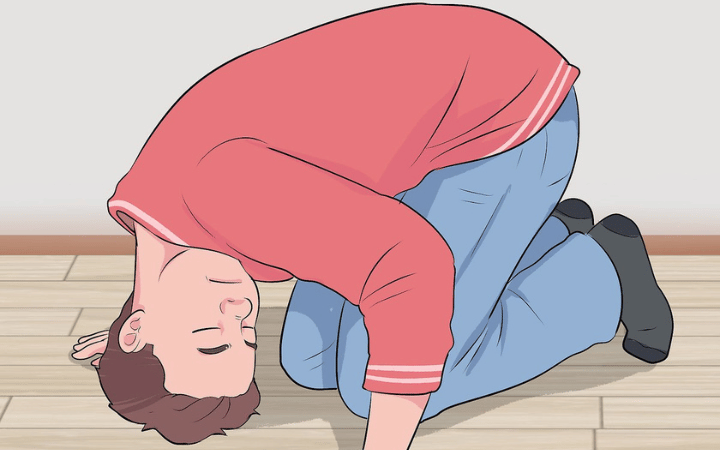
Vertigo can turn the world around you into a dizzying, disorienting experience, impacting your ability to perform daily activities and diminishing your quality of life. This sensation of spinning or feeling like your surroundings are moving when they’re not is more than just uncomfortable—it can be downright debilitating. Fortunately, for those suffering from certain types of vertigo, such as Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), relief may be closer at hand than you think. Among the most effective treatments for this condition are positional exercises, including the renowned Epley Maneuver.
Positional exercises are designed to move the head and body in specific ways that can help alleviate the symptoms of vertigo. The Epley Maneuver, in particular, is a simple yet powerful technique that can be performed at home, often with immediate results. Alongside the Epley Maneuver, there are other exercises that can also offer relief and help individuals regain their sense of balance and stability.
This article aims to demystify the process of performing the Epley Maneuver and other beneficial positional exercises. By understanding how to correctly execute these movements, you can take an active role in managing vertigo symptoms, reducing their frequency and intensity, and navigating your way towards a more balanced, vertigo-free life.
- Understanding Vertigo and BPPV
- The Epley Maneuver
- Other Beneficial Positional Exercises
- Tips for Success and Safety
- Conclusion
Understanding Vertigo and BPPV
Vertigo is more than just feeling dizzy; it’s a specific sensation of spinning or swaying while standing still, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties walking. It can severely affect one’s lifestyle, making simple tasks feel daunting and disrupting daily routines. Vertigo isn’t a disease itself but a symptom of various underlying conditions, the most common being Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV).
What is Vertigo?
Vertigo symptoms include a feeling of spinning, tilting, swaying, unbalanced, or being pulled in one direction. These sensations can last from a few minutes to several hours and may come and go. Activities that involve shifting your head’s position, like tipping your head up or down, can trigger or worsen vertigo episodes. It’s essential to understand these symptoms to effectively recognize and differentiate vertigo from the occasional dizziness or lightheadedness many people experience.
What Causes Vertigo?
While vertigo can stem from various issues, including inner ear problems, Meniere’s disease, vestibular neuritis, or even migraines, BPPV is the most frequent cause.
Understanding BPPV
BPPV occurs when tiny calcium particles (canaliths) clump up in canals of the inner ear. The inner ear sends signals to the brain about head and body movements relative to gravity. It helps you keep your balance. BPPV disrupts this signal, causing vertigo and imbalance. It’s often triggered by specific changes in the position of your head. It’s called “benign” because it’s not life-threatening, “paroxysmal” because it comes in sudden, brief spells, “positional” because it’s triggered by certain head positions, and “vertigo” because the sensation involves a false sense of rotational movement.
Diagnosis and Impact
Diagnosing BPPV typically involves a physical examination and may include tests to check the balance and hearing, as well as the head movements that trigger vertigo. The impact of BPPV on an individual’s life can be significant, affecting not just physical well-being but also emotional health due to the unpredictability of vertigo episodes.
Understanding the nature of vertigo and the specifics of BPPV is crucial for anyone seeking to manage their symptoms effectively. It’s the first step toward finding relief through treatments like the Epley Maneuver and other positional exercises, which will be discussed in the following sections. These maneuvers, when done correctly, can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of vertigo episodes, offering a beacon of hope for those affected by this challenging condition.
The Epley Maneuver
The Epley Maneuver is a simple, yet profoundly effective, positional therapy used to treat BPPV, the most common cause of vertigo originating from the inner ear. Discovered by Dr. John Epley and designed to alleviate the dizzy spells associated with BPPV, this maneuver works by repositioning the tiny calcium carbonate crystals that have moved into the sensitive areas of the inner ear where they don’t belong.
Purpose and Effectiveness
The primary goal of the Epley Maneuver is to move the dislodged canaliths from the semicircular canals back to the utricle of the inner ear, where they can no longer cause vertigo. This is achieved through a series of carefully choreographed movements that are designed to guide the canaliths out of the semicircular canal. Clinical studies have shown that the Epley Maneuver is highly effective, with a success rate of over 90% in treating BPPV.
How to Perform the Epley Maneuver at Home
While it’s advisable to have the maneuver initially demonstrated by a healthcare professional, the Epley Maneuver can be performed at home by following these steps:
1. Start Position: Sit upright on a flat surface, with a pillow behind you and legs extended forward. Turn your head 45 degrees to the side of the affected ear.
2. Lying Back: Quickly lie back, keeping your head turned to the affected side but now at a 30-degree angle so that it is slightly hanging off the edge of the bed. Hold this position for about 30 seconds, or until any vertigo ceases.
3. Head Rotation: Turn your head 90 degrees to the opposite side, holding this new position for another 30 seconds.
4. Body Roll: While maintaining the angle of your head, roll your body onto your side in the direction you’re facing, pausing for another 30 seconds.
5. Sitting Up: Carefully sit up, but remain on the bed for a few moments before standing up to avoid sudden dizziness.
Safety Precautions and When to Avoid
It’s crucial to approach the Epley Maneuver with caution, especially if you have neck or back problems, heart conditions, or issues with blood circulation in the brain. In such cases, or if the maneuver does not relieve your symptoms, consult a healthcare provider. Some individuals might experience mild side effects, such as brief dizziness during the movements.
Conclusion
The Epley Maneuver is a safe and effective treatment for BPPV when performed correctly. It has empowered countless individuals to manage their vertigo symptoms at home. However, if you’re unsure about the procedure or its suitability for your condition, seeking professional guidance is always the best course of action.
In the next section, we’ll explore other positional exercises that can help alleviate vertigo symptoms, offering alternatives and complements to the Epley Maneuver for comprehensive vertigo management.
Other Beneficial Positional Exercises
While the Epley Maneuver is highly effective for many people suffering from BPPV, there are other positional exercises that can also provide relief from vertigo symptoms. These exercises, like the Epley Maneuver, aim to move the dislodged crystals within the inner ear to areas where they can no longer cause vertigo. Here’s an overview of some additional exercises that can be beneficial.
Semont Maneuver
The Semont Maneuver is another technique used to treat BPPV, particularly when the Epley Maneuver is not effective or suitable. This maneuver involves a rapid shift from lying on one side to lying on the other.
- Starting Position: Sit on the edge of your bed and turn your head 45 degrees away from the affected ear.
- First Movement: Lie down quickly on the side of the affected ear. Hold this position for 30 seconds.
- Second Movement: Swiftly move to lie on the opposite side of your initial position without changing the direction of your head. Wait for another 30 seconds.
- Return to Sitting: Sit back up slowly.
Brandt-Daroff Exercises
Brandt-Daroff exercises are a series of movements you can do at home to relieve symptoms of vertigo. They are less specific to BPPV and can be tried if the Epley or Semont maneuvers are not effective.
- Start: Sit upright on the edge of your bed.
- First Move: Lie down on one side with your nose pointed up at about a 45-degree angle. Remain in this position for 30 seconds or until vertigo subsides.
- Return to Start: Sit back up for 30 seconds.
- Second Move: Repeat the movement on the other side.
These exercises should be repeated multiple times a day for several days until vertigo symptoms decrease.
Foster Maneuver (Half Somersault Maneuver)
The Foster Maneuver, or Half Somersault Maneuver, is a newer exercise that some find easier to perform than the Epley or Semont maneuvers.
- Kneel Down: Start by kneeling on the floor.
- Tuck and Look Up: Tuck your head towards your knees, then look up at the ceiling.
- Half Somersault: Place your hands on the ground in front of you, and perform a half somersault, bringing your head in between your knees but keeping your neck extended.
- Turn: Turn your head in the direction of your affected ear, then raise your head to back level, keeping it turned. Finally, raise your head fully upright while keeping it turned to the side.
- Return to Start: Sit back up.
Tips for Success and Safety
While these exercises can be effective, it’s crucial to perform them correctly and safely. Start slowly, and if you experience severe dizziness or vertigo, stop and consult a healthcare professional. It’s also recommended to have someone with you when trying these exercises for the first time.
Conclusion
Positional exercises offer a self-managed approach to alleviating vertigo symptoms. Whether you opt for the Epley Maneuver, the Semont Maneuver, Brandt-Daroff exercises, or the Foster Maneuver, these techniques can significantly improve your quality of life by reducing or eliminating the uncomfortable sensations associated with vertigo. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or if your vertigo symptoms persist.
Tips for Success and Safety
Successfully managing vertigo through positional exercises involves more than just knowing the steps. Here are some essential tips to ensure effectiveness and safety while performing the Epley Maneuver, Semont Maneuver, Brandt-Daroff exercises, or the Foster Maneuver at home.
Start Slowly and Increase Gradually
When you first begin performing these exercises, it’s crucial to start slowly. This approach helps your body adjust to the movements and minimizes the risk of severe dizziness or nausea. As you become more accustomed to the exercises and your symptoms improve, you can gradually increase the frequency and intensity.
Monitor Your Symptoms
Keep a log of your vertigo symptoms before, during, and after the exercises. Monitoring your symptoms can help you identify patterns, understand which exercises are most effective for you, and gauge your progress over time. If your symptoms worsen or do not improve, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional.
Ensure a Safe Environment
Performing exercises that induce or manipulate vertigo symptoms can sometimes lead to loss of balance. Ensure your surroundings are safe and free of obstacles that could cause injury if you were to fall. Performing the exercises on a soft surface such as a bed or a carpeted floor can also help reduce the risk of injury.
Consult a Healthcare Professional
Before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or if your vertigo symptoms are severe, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, demonstrate how to perform the maneuvers safely, and offer alternative treatments if necessary.
Have Someone with You
Especially when performing these exercises for the first time, it’s advisable to have someone with you. This person can help ensure you’re performing the maneuvers correctly, provide support if you become dizzy or unstable, and assist in case of an emergency.
Know When to Seek Further Medical Advice
If you experience severe or persistent symptoms despite performing these exercises, it’s crucial to seek further medical advice. Persistent vertigo could be a sign of a more serious underlying condition that requires professional medical treatment.
Conclusion
Positional exercises are a valuable tool in the management of vertigo symptoms for many individuals. However, success with these exercises requires patience, precision, and a cautious approach to ensure safety and effectiveness. By following these tips and consulting with healthcare professionals as needed, you can maximize the benefits of these exercises while minimizing risks. Implementing these tips for success and safety can empower you to manage your vertigo symptoms more effectively, helping you lead a more comfortable and balanced life.
Conclusion
Navigating through the challenges of vertigo can be a daunting journey, marked by moments of uncertainty and discomfort. However, the availability of positional exercises such as the Epley Maneuver, Semont Maneuver, Brandt-Daroff exercises, and the Foster Maneuver offers a beacon of hope for those seeking relief. These maneuvers, grounded in the principles of vestibular rehabilitation, are designed to provide not only immediate relief from the disorienting symptoms of BPPV but also a pathway towards long-term management of vertigo.
It’s essential to approach these exercises with patience, understanding that the journey to recovery may require time and repeated efforts. Success is not just about performing the exercises but doing so with the right technique, under safe conditions, and with a mindful eye on one’s health and well-being. The tips provided herein aim to enhance the effectiveness of these exercises while ensuring safety, emphasizing the importance of a gradual, monitored approach.
Remember, while these home-based maneuvers offer significant benefits, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice. Persistent or severe vertigo symptoms warrant a consultation with a healthcare provider to rule out underlying conditions and to explore a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
In conclusion, positional exercises represent a powerful tool in the management of vertigo, enabling individuals to reclaim a sense of balance and control over their lives. By integrating these exercises into your routine, under the guidance of a healthcare professional when necessary, you can embark on a path towards reducing vertigo’s impact on your daily life, stepping confidently forward with each maneuver towards stability and well-being.